Cybersecurity on a Budget:
A Small Business Survival Guide Introduction
Running a small business is hard enough without worrying about hackers. But here’s the reality: 43% of cyberattacks target small businesses and many never recover. Despite high awareness, most small businesses still believe they’re too small to be attractive targets for threat actors. Although 79% of small businesses experienced at least one cyber attack in the last five years, 64% still don’t think they’re an attractive target for threat actors. High concern and real experience are not enough for small business leaders to see themselves as high-risk.
Massive IT budgets and enterprise-level software isn’t always necessary. With the right approach, small organizations can build strong cybersecurity on a budget.
Here’s a step-by-step guide.
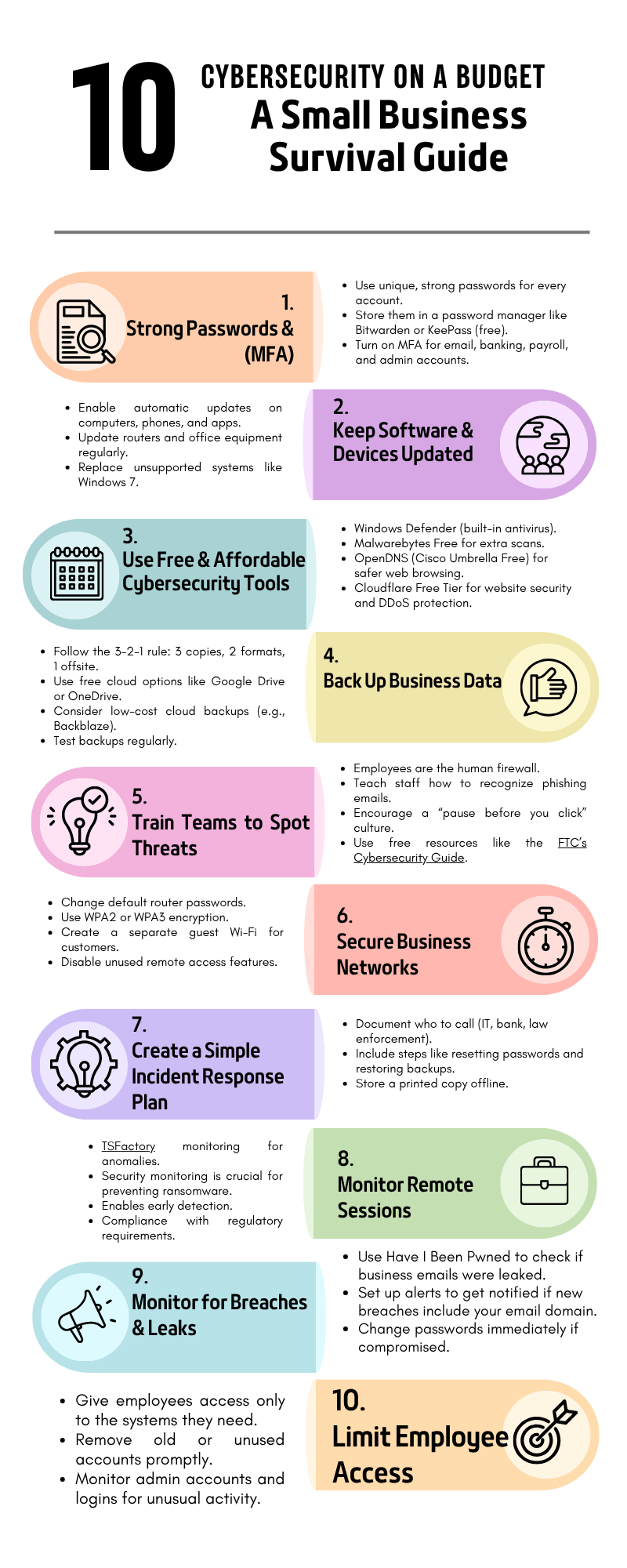
1. Strong Passwords & Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Passwords are the first line of defense. Weak ones are like leaving the front door unlocked.
- Use unique, strong passwords for every account.
- Store them in a password manager like Bitwarden or KeePass (free).
- Turn on MFA for email, banking, payroll, and admin accounts.
Cost: $0
Impact: High
2. Keep Software & Devices Updated
Outdated software is a hacker’s best friend.
- Enable automatic updates on computers, phones, and apps.
- Update routers and office equipment regularly.
- Replace unsupported systems like Windows 7.
Cost: $0
Impact: High
3. Use Free & Affordable Cybersecurity Tools
Solid protection doesn’t need expensive tools.
- Windows Defender (built-in antivirus).
- Malwarebytes Free for extra scans.
- OpenDNS (Cisco Umbrella Free) for safer web browsing.
- Cloudflare Free Tier for website security and DDoS protection.
Cost: Mostly free
Impact: Strong
4. Back Up Business Data
Data loss from ransomware or accidents can be devastating.
- Follow the 3-2-1 rule: 3 copies, 2 formats, 1 offsite.
- Use free cloud options like Google Drive or OneDrive.
- Consider low-cost cloud backups (e.g., Backblaze).
- Test backups regularly.
Cost: Free–Low
Impact: Critical
5. Train Teams to Spot Threats
- Employees are the human firewall.
- Teach staff how to recognize phishing emails.
- Encourage a “pause before you click” culture.
- Use free resources like the FTC’s Cybersecurity Guide.
Cost: Free
Impact: Huge
6. Secure Business Networks
Wi-Fi is a common entry point for attackers.
- Change default router passwords.
- Use WPA2 or WPA3 encryption.
- Create a separate guest Wi-Fi for customers.
- Disable unused remote access features.
Cost: Free
Impact: Strong
7. Create a Simple Incident Response Plan
If something goes wrong, a plan keeps businesses running.
- Document who to call (IT, bank, law enforcement).
- Include steps like resetting passwords and restoring backups.
- Store a printed copy offline.
Cost: Free (just time to prepare)
Impact: Essential
8. Monitor Remote Sessions
- TSFactory monitoring for anomalies.
- Security monitoring is crucial for preventing ransomware.
- Enables early detection.
- Compliance with regulatory requirements.
Cost: Low
Impact: Essential
9. Monitor for Breaches & Leaks
Even strong passwords can be stolen in data breaches. Be proactive.
- Use Have I Been Pwned to check if business emails were leaked.
- Set up alerts to get notified if new breaches include your email domain.
- Change passwords immediately if compromised.
Cost: Free
Impact: Early warning system
10. Limit Employee Access (Principle of Least Privilege)
The fewer people who have access, the smaller your attack surface.
- Give employees access only to the systems they need.
- Remove old or unused accounts promptly.
- Monitor admin accounts and logins for unusual activity.
Cost: Free
Impact: Reduces insider and accidental risks
Final Thoughts
Cybersecurity doesn’t have to be expensive. By focusing on passwords, updates, free tools, backups, staff training, and network security, organizations can reduce risks dramatically – without draining budgets.
Remember: protecting a business now is far cheaper than recovering from a breach later.